HSC Chemistry Guide:
Answering Condensation Polymerisation Questions
This HSC Chemistry Guide serves an extension to the topic of ‘Condensation Polymerisation’ that we have explored in Module 7 HSC Chemistry Syllabus Notes.
We will learn how to identify and draw the monomer(s) that is responsible to create a condensation polymer in two exam-style questions:
Scenario 1: Drawing the monomers when given the polymer structure.
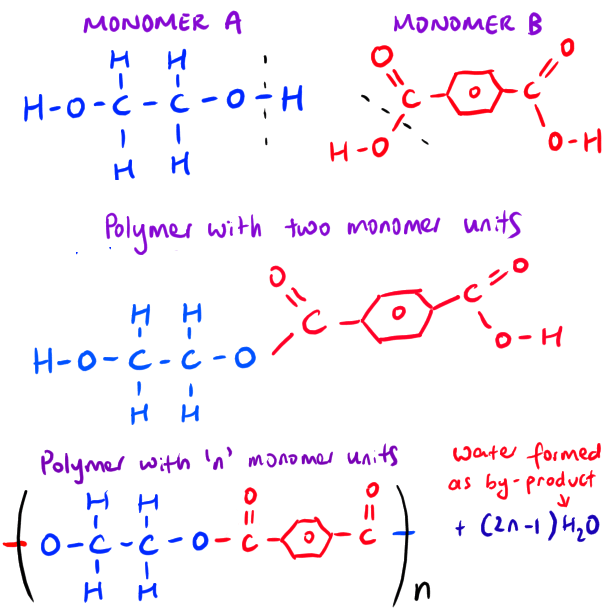
Scenario 2: Drawing the polymer when given the monomers’ structure.
Before we jump into the practical material, let’s do a quick recap on what we have learnt about condensation polymers and polymerisation in Module 7’s Notes.
Framework to draw monomers when given polymer's structure (without C=O bond)
Step 1: Identify the repeating monomer units in the polymer’s structure.
Step 2: Break the C-O-C bond.
Step 3: Draw the repeating units of the monomers.
Step 4: Add H to the monomer that you decide to assign the C-O bond to.
Step 5: Add O-H to the monomer that you only assigned the ‘C’ atom to without the oxygen atom bonded to it.
NOTE: Water is also produced as by product in this case.
Framework to draw monomers when given polymer's structure (with C=O bond)
Step 1: Locate the C=O bond and break it.
Step 2: Identify the repeating monomer units in the polymer’s structure.
Step 3: Break the O=C – O – C bond.
The one monomer takes the C=O and the other monomer takes the C-O bond.
Step 3: Draw the repeating unit of the monomer with the C=O group and the structure of the other monomer with the C-O bond.
Step 4: Add an hydrogen atom to the monomer that you assigned the C-O bond to.
Step 5: Add O-H group to the carbon with the monomer with carbonyl group.
NOTE: Water is also produced as a by-product in this case.
Sometimes, other small molecule can be produced rather than water.
For HSC level, you should just memorise that the OH group comes from the carboxylic acid and NOT from the alcohol. The alcohol only contributes a hydrogen atom.
The reasoning for this has to do with substitution reactions that are taught in Chemistry 1A at university.
Framework to draw monomers when given polymer's structure (with nitrogen atom)
Step 1: Identify the repeating monomer units the polymer’s structure.
Step 2: Break the O=C – N bond.
Step 3: Draw the repeating units of the monomer with the C=O group and the structure of the other monomer with the nitrogen atom.
Step 4: Add a hydrogen atom to the monomer that you assigned the nitrogen atom to.
Step 5: Add a OH group to the monomer that you assigned the C=O group to.
NOTE: Similar to the previous scenario the OH group to make water as a by-product comes from the monomer containing the C=O (Carbonyl) group. The amine group (NH2) only contributes the hydrogen atom.
The reason to this is learnt at first year university chemistry and it is outside the scope of HSC Chemistry.
Moving on! Let’s see if we can do the opposite scenario. Suppose that we can given the monomers and we want to draw the polymer structure!
Drawing polymer involving monomers ONLY O-H group
Drawing polymer involving monomer with C=O group
Drawing polymer involving monomer with N-H bond
NOTE: Water is produced as a by-product in the above example.